Civil Protection Volunteer Service

The Civil Protection Volunteer Service of Madrid was created in 1982 in order to integrate the citizens of Madrid that would like to serve their city as volunteers in the field of Civil Protection.
In 1991 was created the Municipal Assistance and Rescue Emergency Service (SAMUR), focusing on medical assistance in the public areas of Madrid and in mass gatherings or risk situations that could happen.
This kind of activities is closely related to the Civil Protection Volunteer Service, that is why in July, 1994 the Mayor writes a decree that transfers this Volunteer Service to SAMUR. This Decree is endorsed by plenary session of the City Council in June 1997, creating the Civil Defence Department inside SAMUR.
Volunteers Service
The Civil Protection Volunteer Service serves as a connection between Madrid society and the professional resources. With the support and required training, this Service assists in the coverage of public events and high-risk events, in emergency and disaster situations, and also in the training of the population in emergency matters.
To join this Volunteer Service, a course of New Entry has to be taken in order to be enabled to perform tasks and duties of Civil Protection.
In 2007, the Volunteer Service turned 25 years old. During these years the volunteers have served the citizens of Madrid and also beyond our borders, through the special section Disasters Support Unit (DSU).
Civil Protection Department
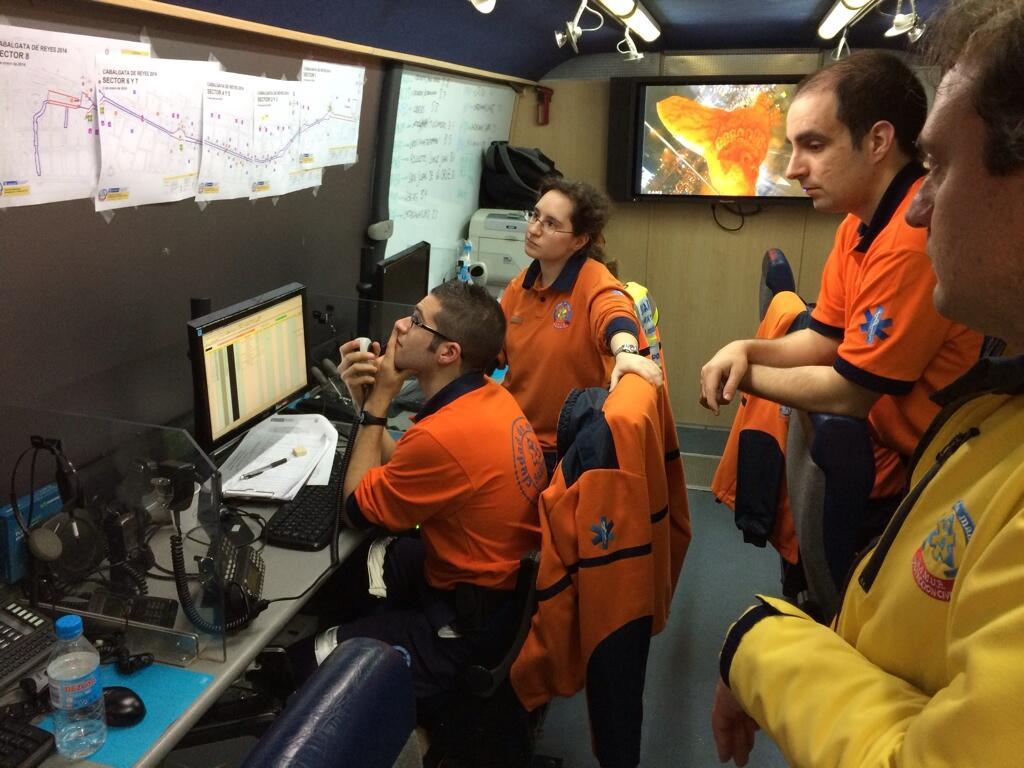
The Civil Protection Department, which belongs to the Deputy Directorate of SAMUR-Civil Protection, manages the Volunteer Service and has two different subsections: the management area and the operational area. The management is carried out by SAMUR-Civil Protection staff, and is responsible for:
-
Planning and design of measures to cover foreseeable risk events.
-
Management of training, both internally , and externally for other professionals and citizens.
-
Management of volunteers, keeping a balance between the number of volunteers joining and leaving the service, and especially the maintenance of an adequately updated training program for the voluntary personnel.
-
Preparation, monitoring and updating of special operative procedures.
-
Logistics is an important part of the Department, so that, it is performed maintenance work, repair, location and study of new products to support medical care in situations of mass casualty incidents, environments or adverse weather conditions, CRBN risk situations, and the required control for this material to be continuously operative.
The operational area is managed by the volunteer human resources office and the Special Procedures Division. There is a senior Emergency Medical Technician in charge of the assessment of the medical care performance of the volunteers and and also has control functions, such as of the scheduled medical coverage services.
The Special Procedures Division examines and modifies special operating procedures, incorporating new means and systems that are tested in coordination with other institutions through periodic drills. The Division also manages the work of the Special Procedures EMT in charge of Logistics Support. Currently it has been introduced the assessment of the performances for these EMT in charge, in order to improve the activity and, if necessary, adjust or modify the operating procedures.
The activity of psychologists in crisis situations is directly linked to this Department. Theis Chief assigns the objectives and the work plan, and the manages the organization of their guards. The presence of the psychologist on duty around the clock provides a better service to the citizen, and it is nowadays a unique reference for other emergency services.
The activity of the Civil Protection Volunteer Service is based on the human and technical training, in order to lead the civil response in situations of serious risk, catastrophe or public calamity (Law 2/1985) and develops according to the following functions:
- Planning and evaluation of foreseeable risks.
- Emergency response, mass casualty incidents and disasters.
- Administrative management.
- Education and training of the volunteers.
- Training of the citizens.